The Knee Joint
The Knee Joint (Articulatio Genus)
Knee Joint Function
The knee is one of the largest and most complex joints in the body. The knee joins the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia). The small bone that runs alongside the tibia (fibula) and the kneecap (patella) are the other bones that make up the knee joint.
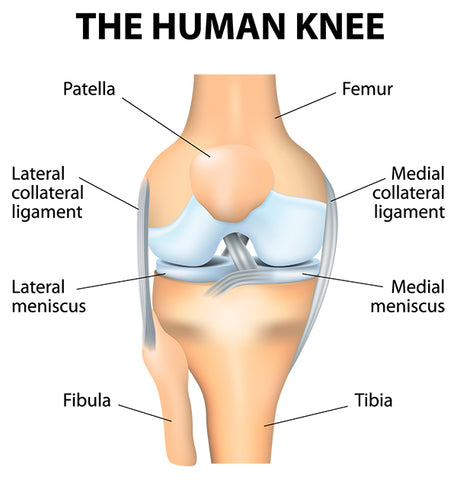
Tendons connect the knee bones to the leg muscles that move the knee joint. Ligaments join the knee bones and provide stability to the knee.
- The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) prevents the femur from sliding backward on the tibia.
- The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) prevents the femur from sliding forward on the tibia.
- The medial (MCL) and lateral (LCL) collateral ligaments prevent the femur from sliding side to side.
Two C-shaped pieces of cartilage called the medial and lateral menisci act as shock absorbers between the femur and tibia. Numerous bursae, or synovial-filled sacs help the knee move smoothly.

Common Injuries of the Knee Joint
Patellofemoral syndrome – irritation of the cartilage on the underside of the kneecap causing knee pain
Osteoarthritis – caused by aging and wear and tear of the cartilage. Symptoms include knee pain, stiffness, and swelling

Knee effusion – fluid buildup inside the knee, usually from inflammation
Meniscal tear – damage to a meniscus, the cartilage that cushions the knee, often occurs with twisting the knee
ACL strain or tear – ACL tear results in knee instability and may require surgical repair
PCL strain or tear – can cause pain, swelling and knee instability, less common than ACL tears, with physical therapy usually the treatment option
MCL strain or tear – may cause pain and possible instability to the inner side of the knee
Patellar tendonitis – inflammation of the tendon connecting the kneecap to the shin bone
Knee bursitis – pain, swelling and warmth in any of the bursae of the knee
Rheumatoid arthritis – an autoimmune condition that can cause arthritis in any joint
Gout – a form of arthritis caused by buildup of uric acid crystals in a joint
Knee Treatments
RICE – Rest (or reduction in activity), Ice, Compression (bandage support) and Elevation
Pain medication – OTC and prescription medication
Physical therapy – strengthens the muscles surrounding the knee
Cortisone injection – injecting steroids to reduce pain and swelling
Hyaluronic acid injections – reduces pain and improves synovial fluid to delay the need for knee surgery

Knee surgery – replace or repair torn ligament, remove an injured meniscus or knee replacement

ACL repair – graft to replace the torn ACL
Nutritional supplements – oral administration of hyaluronic acid, chondroitin, glucosamine, and other nutrients to support joint health and mobility
